Latest News
Speare Memorial Hospital Welcomes Dr. Taylor Augustine to Plymouth OB/GYN
Welcome Dr. Taylor Augustine to Plymouth OB/GYN!
10th Annual Speare Shuffle 5K 2025
What Is Obesity
Obesity is a medical condition where a person has too much body fat, and it can affect their overall health. It’s not just about weight or appearance—obesity can lead to serious health problems and is considered a chronic (long-term) disease.
Why Does Obesity Happen?
There’s no single cause of obesity. It’s often the result of many different factors working together, including:
- Genetics – Your family history can affect how your body stores fat and how it uses energy.
- Hormones and Metabolism – Some people have hormonal or metabolic conditions that make it harder to lose weight.
- Lifestyle Habits – Eating high-calorie foods, being physically inactive, not getting enough sleep, and high stress can all contribute.
- Medications or Health Conditions – Certain medications or illnesses can lead to weight gain.
- Environment – Access to healthy foods, safe places to exercise, and support systems can play a big role.
How Is Obesity Measured?
One common way doctors check for obesity is by using Body Mass Index (BMI), which is a number based on your height and weight. A BMI of 30 or higher usually indicates obesity. However, BMI doesn't tell the whole story—it doesn’t measure muscle, body composition, or where fat is stored in the body.
That’s why our team looks at the bigger picture—including your medical history, lifestyle, lab tests, and other measurements—to fully understand your health.
Find your BMI using the table below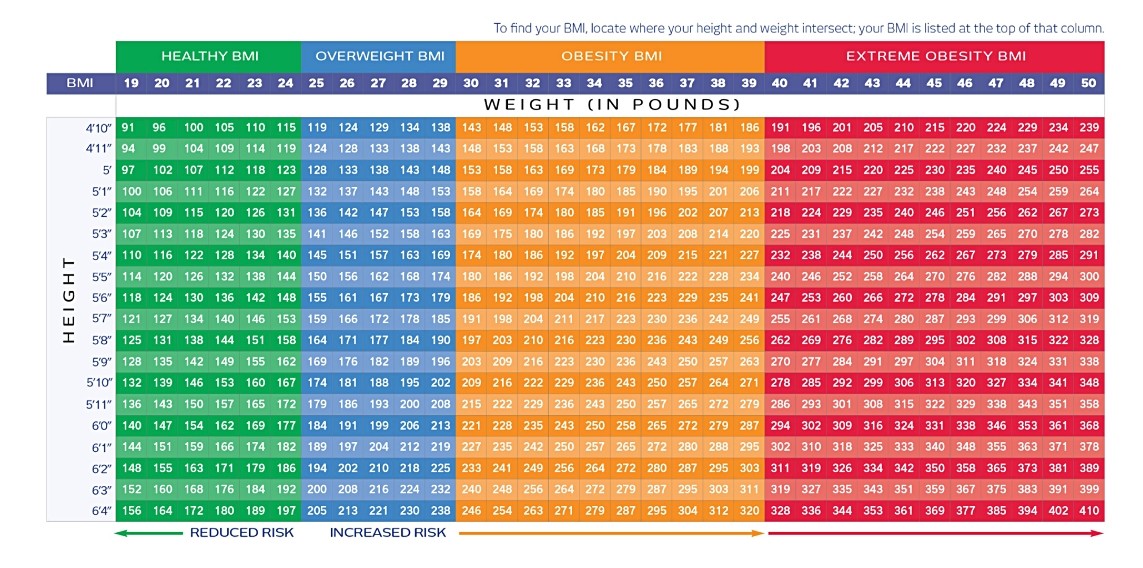
Why Is Obesity Important to Treat?
If left untreated, obesity can raise the risk of many health problems, including:
- Type 2 diabetes
- High blood pressure
- Heart disease
- Sleep apnea
- Joint pain
- Certain cancers
- Depression and anxiety
But the good news is: obesity is treatable and manageable—and small changes over time can lead to big improvements in your health and how you feel.

